|
GR8677 #87
|
|
|
Problem
|
|
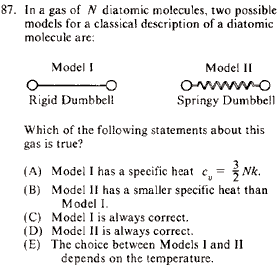 |
Statistical Mechanics }Diatomic Molecules }Diatomic Molecules
Vibrational energy of a diatomic molecule goes to 0 at low temperatures. Thus, the springy dumbbell would be approximately a rigid dumbbell at a low-enough temperature. The other choices are too specific, and thus (E), the most general, must be it.
|
|
|
Alternate Solutions |
smokwzbroiplytowej
2008-10-26 20:53:14 | (Ref. 'Modern Physics 3rd ed, Serway, Moses, Moyer', Chapter 11, p. 378 onward)
(A)
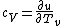
The rigid dumbbell has two rotational degrees of freedom (the rotation around the axis is not 'activated' - see below) each contributing 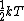 energy (equipartition theorem), so: energy (equipartition theorem), so:
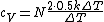
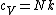
(A) is incorrect
(B) Model II has an additional degree of freedom because of the 'springy' interaction, so by an analogous calculation as above, we see that it has a greater specific heat than Model I - (B) is incorrect as well.
(C) Model I is not always correct. In fact it will fail whenever the vibrations of the molecule become important. Answer (C) is incorrect.
(D) Model II is not always correct either - it fails anytime the potential between the molecules is not approximated correctly by a harmonic potential. Answer (D) is incorrect.
(E) The choice between Models I and II does depend on the temperature, so (E) is correct.
Consider the harmonic potential of Model II. At typical energies: 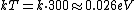 , is low compared to the first excited state of the harmonic oscillator ( , is low compared to the first excited state of the harmonic oscillator (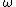 is determined by the particle, for details see the Serway reference) and Model I is a good approximation. For higher temperatures, Model II will be better. is determined by the particle, for details see the Serway reference) and Model I is a good approximation. For higher temperatures, Model II will be better.
---
Note, that classically the rigid dumbbell should have 3 rotational degrees of freedom, because equipartition of energy in the classical model does not need 'activation'. Again, see the Serway chapter. |  |
|
|
Comments |
a
2019-10-15 14:19:21 | Mais avec la finale \'Raw\' fixé pour ce soir, \'Le Phenom\' pourrait émettre une promo audio pour déjouer le match énigmatique échelle Championnat Intercontinental de la WWE au Wyatt.\r\na http://www.ms-el.dk/es18.asp |  | 62a
2016-09-24 16:45:47 | It\'s true that vibration energy of molecules is zero at sufficiently low temperatures, which is the reason why (E) is correct. But it\'s really horrible reasoning to say that the other choices are too specific and the most general choice must be it. If (A) said (5/2)Nk instead of (3/2)Nk, it would still be just as specific but it would be correct.
62a
2016-09-24 16:47:16 |
Or if you interchange \'I\' and \'II\' in (B), then it becomes correct with no loss of specificity.
|
|  | Almno10
2010-11-12 18:56:00 | I will always remember a Stat Mech lecture given to me by Prof. Yoonseok Lee of University of Florida. He had us all drooling over the mystery of the failure of the equipartition theorem to give heat capacities at low T.
"...it seems as if at low temperature, certain degrees of freedom are frozen out..."
|  | tau1777
2008-11-04 15:54:40 | elimination
a) model I has five degrees of freedom, 3 translational and 2 rotational. specific heat at constant volume should be degrees of freedom/2 (Nk) , getting this from specific heat is temperature derivative of U (internal energy) also only at constant volume.
b) model II has 2 extra vibrational degrees of freedom than model I because of spring, so specific heat is 7/2Nk.
c) and d) if this were true why have two models
e) there's you're answer.
IRFAN
2011-08-18 02:37:12 |
justify how 7 degrees of freedom in case of spring??????????
|
|  | smokwzbroiplytowej
2008-10-26 20:53:14 | (Ref. 'Modern Physics 3rd ed, Serway, Moses, Moyer', Chapter 11, p. 378 onward)
(A)
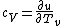
The rigid dumbbell has two rotational degrees of freedom (the rotation around the axis is not 'activated' - see below) each contributing 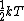 energy (equipartition theorem), so: energy (equipartition theorem), so:
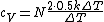
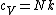
(A) is incorrect
(B) Model II has an additional degree of freedom because of the 'springy' interaction, so by an analogous calculation as above, we see that it has a greater specific heat than Model I - (B) is incorrect as well.
(C) Model I is not always correct. In fact it will fail whenever the vibrations of the molecule become important. Answer (C) is incorrect.
(D) Model II is not always correct either - it fails anytime the potential between the molecules is not approximated correctly by a harmonic potential. Answer (D) is incorrect.
(E) The choice between Models I and II does depend on the temperature, so (E) is correct.
Consider the harmonic potential of Model II. At typical energies: 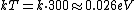 , is low compared to the first excited state of the harmonic oscillator ( , is low compared to the first excited state of the harmonic oscillator (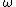 is determined by the particle, for details see the Serway reference) and Model I is a good approximation. For higher temperatures, Model II will be better. is determined by the particle, for details see the Serway reference) and Model I is a good approximation. For higher temperatures, Model II will be better.
---
Note, that classically the rigid dumbbell should have 3 rotational degrees of freedom, because equipartition of energy in the classical model does not need 'activation'. Again, see the Serway chapter.
BerkeleyEric
2010-09-12 16:24:34 |
I think it would actually 5/2 Nk for choice (A) since there are three translational degrees of freedom, too.
|
|  |
|
|
|
|
The Sidebar Chatbox...
Scroll to see it, or resize your browser to ignore it... |
|
|
|
